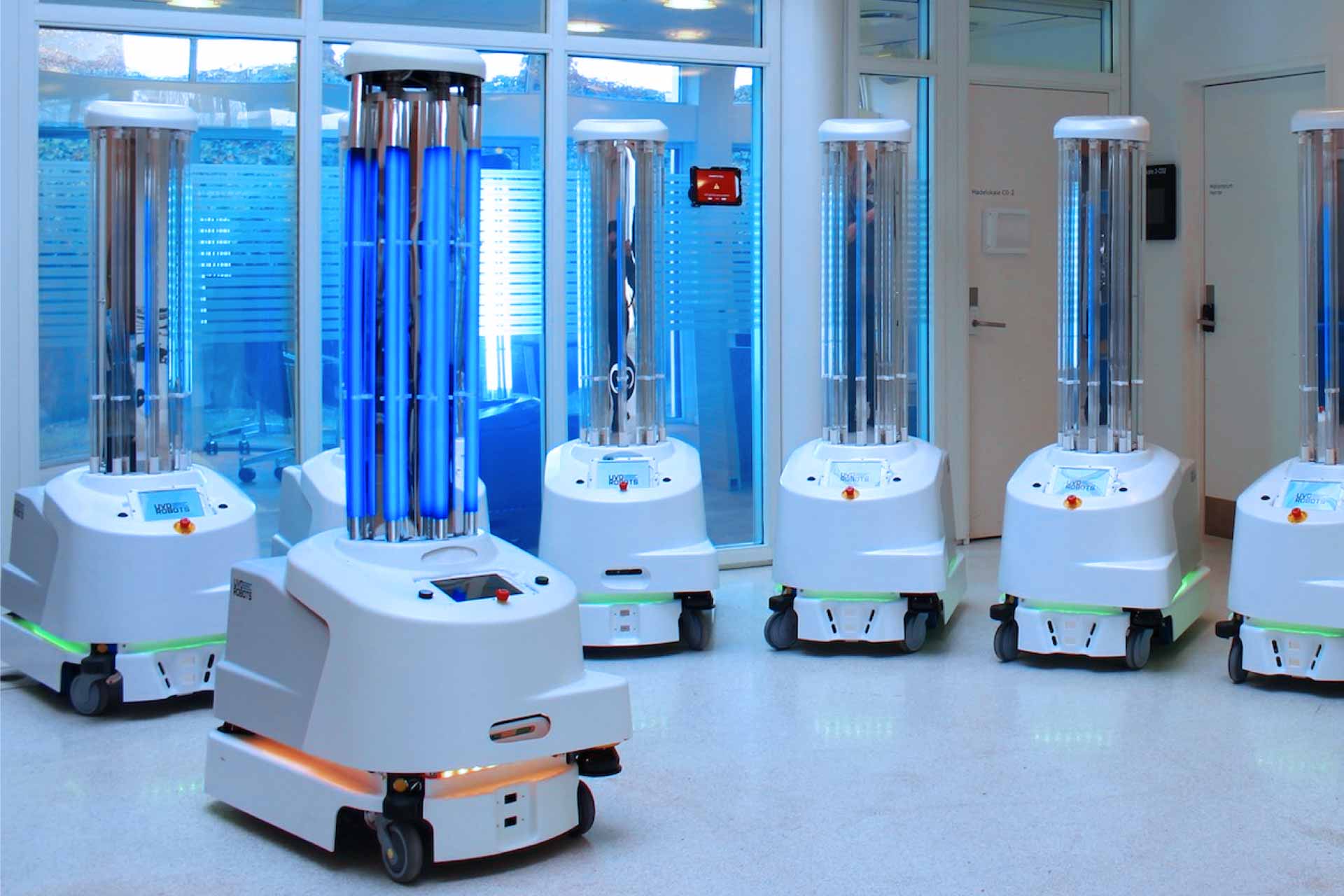
Two Slovenian hospitals received two of the first EU robots to disinfect patient rooms, thus helping reduce and contain the spread of coronavirus. A further 29 disinfection robots are deployed to hospitals in Belgium, Denmark, Germany, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, Spain, Croatia, Lithuania, Luxembourg and the Netherlands.
European Commission purchased these robots which can disinfect a standard size patient room in as quickly as 10 minutes. They use UV ultraviolet light and disinfect over 18 rooms in one charge. The aim is to ensure a sterile environment in hospitals without exposing staff to unnecessary risk. Since this is a physical process rather than one using a chemical disinfectant, it is safer for the hospital staff as they do not need to handle, transport or store toxic, hazardous or corrosive chemicals anymore.
UV disinfection robots
Cleaning staff operate the robot remotely via a mobile application and the operation is started from outside the room to be disinfected, so no healthcare worker is present during the process. Supplied by the Danish company UVD Robots, which won an emergency procurement tender, the devices are part of the Commission’s effort to provide useful and necessary equipment to Member States in aid of tackling the pandemic. In total, €12 million are available from the Emergency Support Instrument to purchase 200 robots.
Robotics supports Europe’s digital future
The importance of robotics lies in its wide-ranging impact on Europe’s capacity to maintain and expand a competitive manufacturing sector with millions of related jobs at stake. Robotics also offers new solutions to societal challenges from ageing to health, smart transport, security, energy and environment.
Robots in Healthcare: Debating Ethics in Health and AI technology
The European Commission actively promotes research, job creation and innovation through better and safer robots, while safeguarding ethical aspects of the progress achieved. The European Commission’s focus is on building on our continuous effort to develop excellent scientific base for pushing the limits of the technology, and exploiting such results in real world applications.